Maker Culture: DIY’s Impact on US Innovation and Subcultures
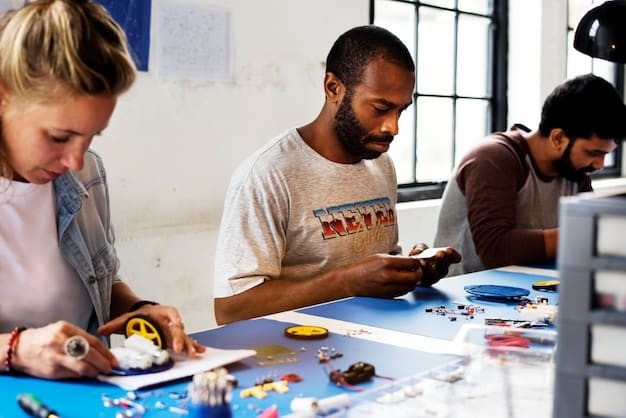

Maker culture, rooted in do-it-yourself (DIY) principles, is significantly influencing innovation and shaping subcultures across the United States by fostering creativity, collaboration, and technological advancement.
The maker culture is more than just a hobby; it’s a movement that’s reshaping how we think about innovation and community in the United States. From tech enthusiasts to crafters, DIY is driving significant changes in industries and local subcultures.
Understanding Maker Culture in the US
Maker culture in the US is a contemporary subculture that celebrates hands-on creation and learning. It’s about more than just making things; it’s about sharing knowledge, collaborating on projects, and empowering individuals to bring their ideas to life.
This culture is fueled by access to technology like 3D printers, laser cutters, and microcontrollers, making it easier than ever for people to design and build their own products. The rise of online communities and platforms has further amplified the maker movement, connecting creators from all over the country.
The DIY Ethos
At the heart of maker culture is the DIY ethos, which encourages individuals to take control of their creative processes. This mindset fosters a sense of self-reliance and problem-solving, as makers learn to troubleshoot issues and adapt their designs as needed.
Key Components of Maker Culture
- Accessibility: Technology and resources are becoming more accessible to the general public.
- Community: Makerspaces and online forums provide platforms for sharing ideas and collaborating.
- Education: Learning is hands-on and project-based, fostering practical skills.
In summary, understanding maker culture involves recognizing its emphasis on hands-on creation, community collaboration, and accessible technology, all underpinned by the DIY ethos. These elements combine to form a dynamic force that’s reshaping innovation and subcultures across the US.
The Influence of Makerspaces
Makerspaces are community workshops that provide access to tools, equipment, and expertise. They serve as hubs for maker culture, fostering collaboration, innovation, and skill-sharing. These spaces play a crucial role in democratizing access to technology and promoting hands-on learning.
By offering a wide range of equipment, from 3D printers to sewing machines, makerspaces enable individuals to explore diverse interests and develop new skills. They also create a supportive environment where makers can connect with like-minded individuals, exchange ideas, and work together on projects.

Educational Opportunities
Many makerspaces offer workshops, classes, and mentorship programs that cater to both beginners and experienced makers. These educational opportunities help to build a skilled workforce and promote lifelong learning.
Economic Impact
Makerspaces can also contribute to economic development by supporting startups and small businesses. By providing access to prototyping equipment and business resources, these spaces help entrepreneurs bring their ideas to market.
- Skill Development: Offers opportunities to learn new technical and creative skills.
- Community Building: Connects individuals with shared interests and fosters collaboration.
- Entrepreneurship: Supports startups and small businesses with resources and equipment.
In conclusion, makerspaces are essential to the growth and influence of maker culture by offering accessible resources, educational opportunities, and entrepreneurial support. Their impact extends beyond individual projects, contributing to economic and community development.
DIY Electronics and Robotics
DIY electronics and robotics are significant components of maker culture, empowering individuals to design, build, and program their own electronic devices and robots. This hands-on approach fosters a deep understanding of technology and encourages innovation.
From building custom drones to creating interactive art installations, DIY electronics and robotics projects span a wide range of applications. The availability of open-source hardware platforms like Arduino and Raspberry Pi has made it easier than ever for makers to get started with these technologies.
Arduino and Raspberry Pi
Arduino is a microcontroller board that can be programmed to control electronic components like LEDs, sensors, and motors. Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer that can run a full operating system, making it suitable for more complex projects.
Applications in Education
DIY electronics and robotics are increasingly being used in educational settings to teach STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) concepts. These hands-on projects engage students and help them develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Creative Expression: Enables makers to create unique and personalized electronic projects.
- STEM Education: Provides hands-on learning opportunities in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.
- Problem-Solving: Encourages makers to troubleshoot and find solutions to technical challenges.
In sum, DIY electronics and robotics are transforming the way people interact with technology. By empowering individuals to design and build their own devices, this aspect of maker culture fosters innovation, education, and creative expression.
The Role of 3D Printing in Maker Culture
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized maker culture by enabling individuals to create three-dimensional objects from digital designs. This technology has made it easier than ever to prototype ideas, customize products, and produce complex geometries.
From printing replacement parts for household appliances to creating intricate art pieces, 3D printing has a wide range of applications in maker culture. The increasing affordability of 3D printers has further democratized access to this technology, allowing more people to participate in the maker movement.
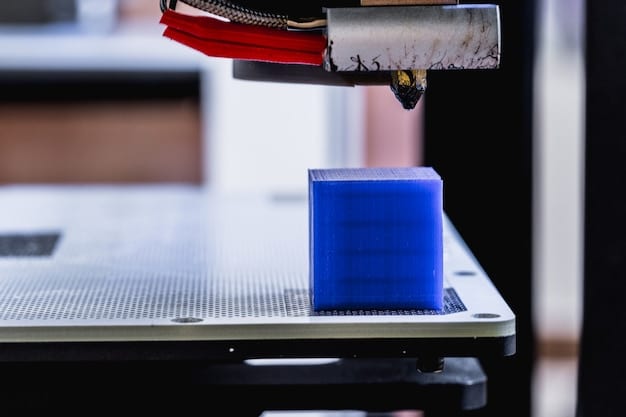
Prototyping and Customization
3D printing is particularly useful for prototyping new products and customizing existing ones. Makers can quickly iterate on designs and create personalized items tailored to their specific needs.
Impact on Manufacturing
3D printing is also having a significant impact on manufacturing, enabling small-scale production and on-demand manufacturing. This technology allows makers to create and sell their own products without the need for large-scale manufacturing facilities.
- Rapid Prototyping: Enables makers to quickly create and test new designs.
- Customization: Allows for the creation of personalized products tailored to individual needs.
- Small-Scale Manufacturing: Facilitates the production of small batches of products without large investments.
To summarize, 3D printing has become an indispensable tool in maker culture, fostering innovation, customization, and small-scale manufacturing. Its accessibility and versatility have made it a key driver of the DIY movement.
Maker Culture and Education
Maker culture is increasingly recognized for its educational value, offering hands-on learning experiences that complement traditional classroom instruction. Integrating maker activities into education can foster creativity, problem-solving skills, and critical thinking.
From elementary schools to universities, educators are incorporating maker-centered learning into their curricula. These activities can range from simple crafts to complex engineering projects, depending on the age and skill level of the students.
Benefits of Maker-Centered Learning
Maker-centered learning encourages students to take ownership of their learning, experiment with new ideas, and collaborate with their peers. This approach can also help to bridge the gap between theory and practice, making learning more relevant and engaging.
Examples of Maker Education Programs
- Robotics Clubs: Students design, build, and program robots to compete in challenges.
- 3D Printing Workshops: Students learn to design and print their own objects using 3D printers.
- Coding Camps: Students learn to write computer code and develop software applications.
In conclusion, maker culture plays a vital role in education by providing hands-on learning experiences that foster creativity, problem-solving skills, and critical thinking. By integrating maker activities into curricula, educators can prepare students for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
The Future of Innovation through Maker Culture
The future of innovation is deeply intertwined with maker culture, as the DIY movement continues to empower individuals to create, invent, and solve problems in new and innovative ways. This culture fosters a spirit of experimentation and collaboration that is essential for driving technological advancement.
As technology becomes more accessible and affordable, maker culture is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of innovation. From grassroots inventions to disruptive startups, the maker movement is fueling creativity and entrepreneurship across the United States.
Trends Shaping the Future of Maker Culture
Several trends are shaping the future of maker culture, including the growth of online communities, the increasing availability of open-source resources, and the rise of crowdfunding platforms.
Implications for Industries
As maker culture continues to evolve, it is likely to have a profound impact on a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to education and entertainment. By fostering innovation and creativity, the maker movement is helping to create a more dynamic and resilient economy.
- Democratization of Innovation: Empowers individuals to create and invent without traditional gatekeepers.
- Open-Source Collaboration: Fosters a culture of sharing and collaboration among makers.
- Economic Opportunities: Creates new opportunities for entrepreneurs and small businesses.
In summary, maker culture is a powerful force for innovation, driving technological advancement and fostering a spirit of creativity and collaboration. As this culture continues to grow and evolve, it is likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the United States and beyond.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 💡 DIY Ethos | Empowering individuals to create and innovate. |
| 🏢 Makerspaces | Community hubs offering tools and expertise. |
| 🤖 DIY Electronics | Building custom devices using Arduino and Raspberry Pi. |
| 🖨️ 3D Printing | Creating prototypes and customized products. |
Frequently Asked Questions
▼
Maker culture is a contemporary subculture centered around hands-on creation, DIY projects, and the sharing of knowledge and resources. It emphasizes learning through doing and fostering a spirit of innovation.
▼
Makerspaces provide access to tools, equipment, and expertise, enabling individuals to prototype ideas, experiment with different technologies, and collaborate on projects. This fosters a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship.
▼
Examples include building custom drones, creating interactive art installations, designing wearable technology, and programming robots. These projects often involve using platforms like Arduino and Raspberry Pi for control and automation.
▼
3D printing enables makers to create three-dimensional objects from digital designs, allowing them to prototype new products, customize existing ones, and produce complex geometries. It’s used for everything from replacement parts to art pieces.
▼
Maker culture provides hands-on learning experiences that foster creativity, problem-solving skills, and critical thinking. It complements traditional classroom instruction and prepares students for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
Conclusion
In summary, maker culture is a dynamic and evolving movement that is significantly influencing innovation and shaping subcultures across the United States. By empowering individuals to create, collaborate, and learn through hands-on experiences, maker culture is driving technological advancement, fostering entrepreneurship, and transforming education.





